- Introduction & Syllabus
- 1. Front End Fundamentals
- 2. Object-Oriented Javascript
- 3. Project #1
- 4. Ruby
- 5. Full Stack Sinatra
- 6. Project #2
-
7.
Ruby on Rails
- 7.1. Developer Workflow
- 7.2. Digital Ocean/PaaS
- 7.3. Digital Ocean Lab
- 7.4. Building a webserver
- 7.5. Getting started with Rails
- 7.6. Rails Model Attributes
- 7.7. Rails File Structure
- 7.8. Sinatra vs Rails
- 7.9. Rails Generate Lab
- 7.10. Day 1 - After Hours
- 7.11. Rails Form Helpers
- 7.12. Rails Form Helpers Lab
- 7.13. Authentication
- 7.14. Videos & Source Code
- 8. Underscore.js
- 9. Backbone.js
- 10. Project #3
- 11. Node, Express.js, MongoDB
- 12. Angular.js & TDD
- 13. Portfolio Project
- Published with GitBook
Introduction to Node
Getting Started
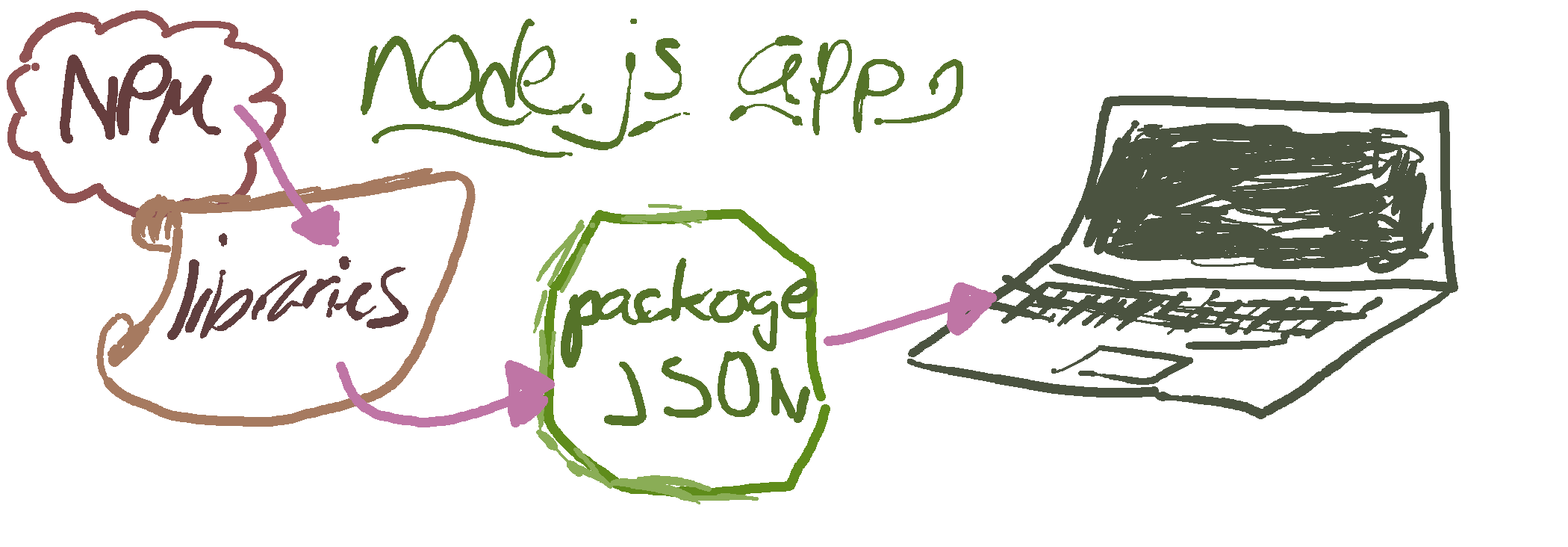
1. package.json
We're going to create a package.json file for our new application. This contains information about your app, such as:
- Application's name
- Author
- Git(hub) repository
- Current version
- License And in the future, it will also save any dependancies your application may have.
Let's Give it a Try
- To get started, create a new project folder. Change directory to that folder.
- Next, create an empty Javascript file to host our application:
touch app.js - Then, enter the following command:

- That's right:
npm init
You'll be prompted through a variety of questions, such as:
name: an_api
version: (1.0.0) 0.1.0
description: My first express api
entry point: (index.js) app.js
test command:
git repository: https://github.com/code-for-coffee/express_api
keywords:
author: your-user-name
license: (ISC) MIT
This generates the following package.json file:
{
"name": "Tasker",
"version": "0.1.0",
"description": "The MEAN way to track your Tasks!",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "https://github.com/code-for-coffee/Tasker"
},
"author": "code-for-coffee",
"license": "MIT",
"bugs": {
"url": "https://github.com/code-for-coffee/Tasker/issues"
},
"homepage": "https://github.com/code-for-coffee/Tasker"
}
2. Setting Application dependancies
Use npm install <pkg> --save afterwards to install a package and save it as a dependency in the package.json file.
We're going to be using the following dependancies in our MEAN application:
- Express.js
- MongoDB
- Angular.js
To get started, let's go ahead and add Express.js to our project by running the following command:
npm install express --save
- Once you run this command, a dependency object will be created inside of your
package.json. Go ahead - take a look! - It looks like this, right?
"dependencies": { "express": "^4.12.4" } - All node package files are saved to
node_modules. - If provided a
package.jsonfile from another project, you can run thenpm installcommand to fetch/install the required packages for that app!
3. Installing the Express 4.0 Application Generator
We want to be able to generate applications in the same way that Ruby on Rails can. We're going to run a command to install an Express.js application generator:
sudo npm install -g express-generator
We'll touch more on this later.
4. Make sure we're all set
We're going to run a few commands to make sure we have the required dependencies for our application:
node --version #checks node version
npm --version #checks npm version
express --version #checks express version